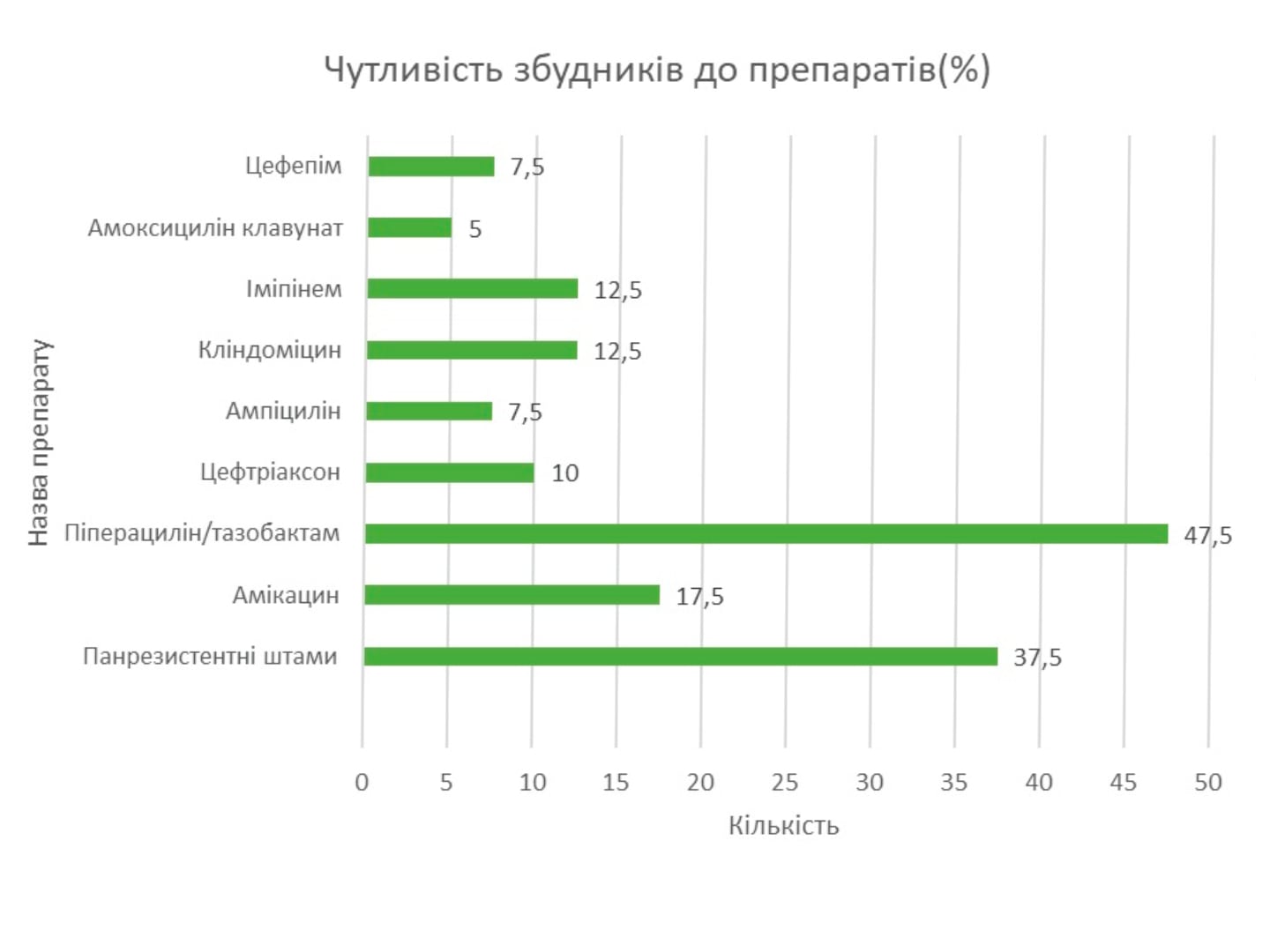
Multicenter study of the effectiveness of postoperative pain relief in Ukraine using paracetаmol in surgical hospitals – “ROZUM”
Orthopaedic Trauma, Surgeon, The anesthesiologist and specialist on medical emergency conditions
Abstract. This article is devoted to the effectiveness of postoperative pain relief in surgical hospitals in Ukraine. Multicenter study of the effectiveness of postoperative pain relief in Ukraine using paracetаmol in surgical hospitals – ROZUM is descibed. The effectiveness of multimodal anal gesia and other analgesia in the postoperative period has been determined. Predictors of inadequate pain relief in surgical patients were identified, and the risks of pain syndrome development in a surgical hospital were assessed. The use of paracetamol in the schemes of multimodal analgesia in the postoperative period was evaluated.
Key words: paracetamol, analgesia, postoperative period, multimodal analgesia.
Authors:
Dmitriev D. V. et al.
Literature:
- Beecher HK. Experimental Pharmacology and MeasureBeech- er HK. Experimental Pharmacology and Measurement of the Subjective Response. Science [Internet]. American Asso- ciation for the Advancement of Science (AAAS); 1952 Aug 15;116(3007):157–62. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1126/ science.116.3007.157
- Beecher HK. The measurement of pain: prototype for the quantitative study of subjective responses. Pharmacological reviews. 1957 Mar 1;9(1):59-209.
- Beecher HK. Measurement of subjective responses: quantita- tive effects of drugs.
- Mehlisch DR. Review of the comparative analgesic efficacy of sa- licylates, acetaminophen, and pyrazolones. The American Jour- nal of Medicine [Internet]. Elsevier BV; 1983 Nov;75(5):47–52. Available from: https://doorg/10.1016/0002-9343(83)90232-2
- VANE JR. Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis as a Mecha- nism of Action for Aspirin-like Drugs. Nature New Biology [Internet]. Springer Science and Business Media LLC; 1971 Jun;231(25):232–5. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/ newbio231232a0
- Hart FD, Huskisson EC. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Drugs [Internet]. Springer Science and Business Me- dia LLC; 1984 Mar;27(3):232–55. Available from: https://doi. org/10.2165/00003495-198427030-00004
- O’Brien WM. Pharmacology of nonsteroidal anti-inflamma- tory drugs. The American Journal of Medicine [Internet]. El- sevier BV; 1983 Oct;75(4):32–9. Available from: https://doi. org/10.1016/0002-9343(83)90326-1
- Castles JJ, JJ C, JL S. Comparative efficacy and safety of naprox- en and ibuprofen in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Davies EF, Avery GS. Ibuprofen. Drugs [Internet]. Springer Science and Business Media LLC; 1971;2(5):416–46. Available from: https://doorg/10.2165/00003495-197102050-00002
- Giansiracusa JE, Donaldson MS, Koonce ML, Lefton TE, Ruoff GE, Brooks CD. Section 1 Ibuprofen in osteoarthriti Current Medical Research and Opinion [Internet]. Informa Healthcare; 1975 Jan;3(8):481–4. Available from: https://doi. org/10.1185/03007997509110578
- Lanza FL. Endoscopic Studies of Gastric and Duodenal Injury after the Use of Ibuprofen, Aspirin, and Other Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents. The American Journal of Medi- cine [Internet]. Elsevier BV; 1984 Jul;77(1):19–24. Available from: https://doorg/10.1016/s0002-9343(84)80014-5
- OWEN-SMITH BD, BURRY HC. IBUPROFEN IN THE MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOARTHROSIS OF THE HIP. Rheumatology [Internet]. Oxford University Press (OUP); 1972;11(6):281–6. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/ rheumatology/11.6.281
- Ruoff G, RL P. Aspirin-acetaminophen vs ibuprofen in a con- trolled multicenter double-blind study with patients experi- encing pain associated with osteoarthritis.
- Shapiro SS, SS S. The effect of ibuprofen in the treatment of dysmenorrhea.
- Corson SL, Bolognese RJ. Ibuprofen therapy for dysmen- orrhea. The Journal of reproductive medicine. 1978 May 1;20(5):246-52.
- MILSOM I, ANDERSCH B. Effect of ibuprofen, naproxen so- dium and paracetamol on intrauterine pressure and menstru- al pain in dysmenorrhoea. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 1984 Nov;91(11):1129-35.
- Bourne MS. The effect on healing of analgesic and anti-in- flammatory therapy. British journal of sports medicine. 1980 Mar;14(1):26.
- MUCKLE DS. Comparative study of ibuprofen and aspirin in soft-tissue injuries. Rheumatology [Internet]. Oxford Univer- sity Press (OUP); 1974;13(3):141–7. Available from: https:// doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/13.3.141
- Cooper SA, PECHEUR H, Rauch D, Rosenheck A, Ladov M, ENGEL J. The analgesic efficacy of ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen with codeine. InJOURNAL OF DENTAL RE- SEARCH 1984 Jan 1 (Vol. 63, pp. 311-311). 1619 DUKE ST, AL- EXANDRIA, VA 22314: AMER ASSOC DENTAL RESEARCH.
- Beaver WT, Forbes JA, Barkaszi BA, Ragland RN, Hankle JJ. An evaluation of ibuprofen and acetaminophen in postoper- ative oral-surgery pain. Inclinical pharmacology & therapeu- tics 1987 Feb 1 (Vol. 41, No. 2, pp. 180-180). 11830 WEST- LINE INDUSTRIAL DR, ST LOUIS, MO 63146-3318: MOS- BY-YEAR BOOK INC.
- Cooper SA. Five Studies on Ibuprofen for Postsurgical Den- tal Pain. The American Journal of Medicine [Internet]. El- sevier BV; 1984 Jul;77(1):70–7. Available from: https://doi. org/10.1016/s0002-9343(84)80022-4
- Winter L, JG P. A double-blind, comparative evaluation of acetaminophen, caffeine, and the combination of acetamin- ophen and caffeine in outpatients with post-operative oral surgery pain.
- Statistical Aspects of the Analysis of Data From Retrospective Studies of Disease. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer In- stitute [Internet]. Oxford University Press (OUP); 1959 Apr; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/22.4.719
- Armitage P, Berry G, Matthews JN. Statistical methods in medical research. John Wiley & Sons; 2008 Apr 15.
- Van Elteren PH. On the combination of independent two sam- ple tests of Wilcoxon. Bull Inst Intern Staist. 1960;37:351-61.
- Neter J, Wasserman W, Kutner MH. Applied Linear Statistical Models (Homewood, IL: Irwin). NeterApplied Linear Statis- tical Models1985.
- SAS R. NC. SAS User’s Guide: Statistics. Cary, NC.
- DIONNE RA, CAMPBELL RA, COOPER SA, HALL DL, BUCKINGHAM B. Suppression of postoperative pain by preoperative administration of ibuprofen in comparison to placebo, acetaminophen, and acetaminophen plus codeine. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 1983 Jan;23(1):37-43.
- KANTOR TG. Ibuprofen. Annals of Internal Medicine [Inter- net]. American College of Physicians; 1979 Dec 1;91(6):877. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-91-6-877
- Busson M. Update on Ibuprofen: Review Article. Journal of International Medical Research [Internet]. SAGE Publica- tions; 1986 Mar;14(2):53–62. Available from: https://doi. org/10.1177/030006058601400201
- Miller RR. Evaluation of the Analgesic Efficacy of Ibupro Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy [Internet]. Wiley; 1981 Jul 8;1(1):21–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1875-9114.1981.tb03550.x
- Laska EM, Sunshine A, Marrero I, Olson N, Siegel C, Mc- Cormick N. The correlation between blood levels of ibupro- fen and clinical analgesic response. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics [Internet]. Springer Science and Business Media LLC; 1986 Jul;40(1):1–7. Available from: https://doi. org/10.1038/clp1986.129
- Dmytriiev D. Assessment and treatment of postoperative pain in children. Anaesthesia, Pain & Intensive Care. 2019 Jan 18:392-400.
- Dmytriiev D, Dmytriiev K, Stoliarchuk O, Semenenko Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: what do we know about pain management? A narrative review. Anaesthesia, Pain & Intensive Care. 2019 Jul 3;23(1).