Effect of a Novel Free Radical Scavenger, Edaravone (MCI-186), on Acute Brain Infarction
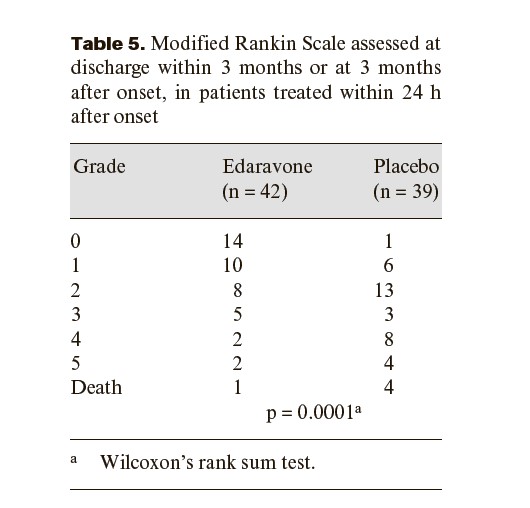
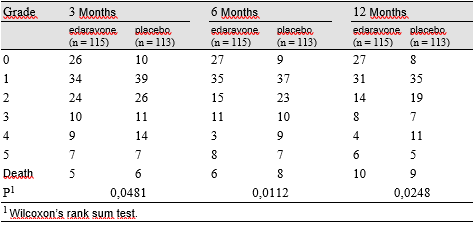
Edaravone, a novel free radical scavenger, demonstrates neuroprotective effects by inhibiting vascular endothelial cell injury and ameliorating neuronal damage in ischemic brain models. The present study was undertaken to verify its therapeutic efficacy following acute ischemic stroke. We performed a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study on acute ischemic stroke patients commencing within 72 h of onset. Edaravone was infused at a dose of 30 mg, twice a day, for 14 days. At discharge within 3 months or at 3 months after onset, the functional outcome was evaluated using the modified Rankin Scale. Two hundred and fifty-two patients were initially enrolled. Of these, 125 were allocated to the edaravone group and 125 to the placebo group for analysis. Two patients were excluded because of subarachnoid hemorrhage and disseminated intravascular coagulation. A significant improvement in functional outcome was observed in the edaravone group as evaluated by the modified Rankin Scale (p = 0.0382). Edaravone represents a neuroprotective agent which is potentially useful for treating acute ischemic stroke, since it can exert significant effects on functional outcome as compared with placebo.
Keywords: clinical trial; free radical; neuroprotection; acute stroke