Pathogenetic pancreoprotection in diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetes is an important medical and social problem, as it develops in each of the 11 adult inhabitants of the planet. In the complicated course of diabetes mellitus, ketoacidosis develops, which is the most common manifestation of acute hyperglycemia in people with both types of diabetes mellitus. The purpose of this study is to systematize and summarize current scientific data on clinically proven methods of drug correction of diabetic ketoacidosis.
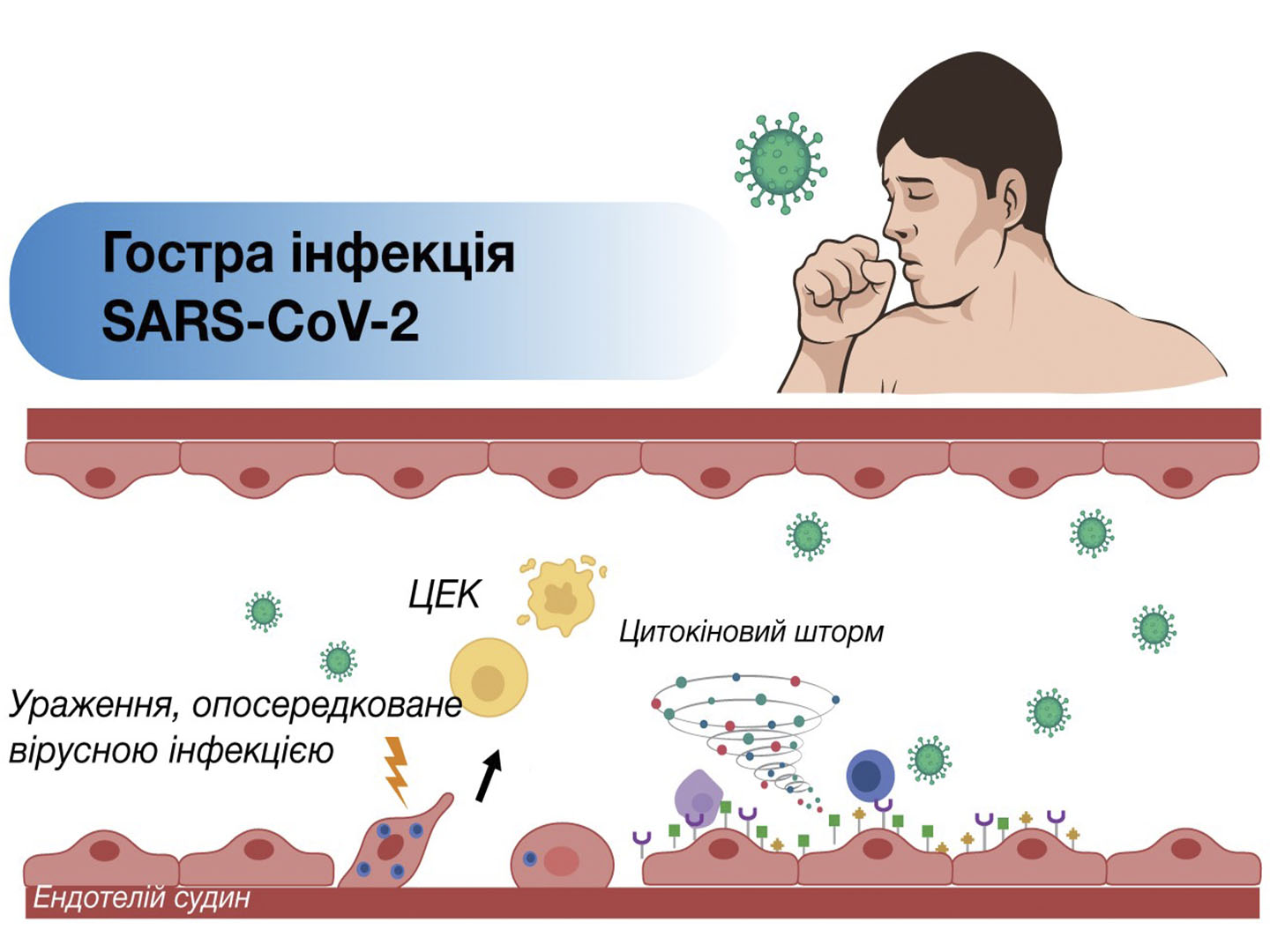
The article presents scientific data on the current state and prospects for the use of effective and safe means of pathogenetic correction of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: Xylat® as an insulin-independent energy source reduces the load on the pancreas; use of Tivortin® provides a protective effect on the vessels of the pancreas and increases insulin sensitivity in insulin resistance.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus, ketoacidosis, pancreatoprotection, L-arginine, xylitol.
Authors:
Sokolova L.K., MD, Professor, V.P. Komisarenko Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
Literature:
- American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care in the Hospital: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019 Jan. 42 (Suppl. 1). 173-181. doi: 10.2337/dc19-S015.
- Borucki K., Aronica S., Starke I., Luley C., Westphal S. Addition of 2.5g l-arginine in a fatty meal prevents the lipemia-induced endothelial dysfunction in healthy volunteers. Atherosclerosis. 2009. 205(1). 251-4.
- Chukwuma C.I., Islam S. Xylitol improves anti-oxidative defense system in serum, liver, heart, kidney and pancreas of normal and type 2 diabetes model of rats. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017 May. 74(3). 817-826.
- Dabelea D., Rewers A., Stafford J.M., Standiford D.A., Lawrence J.M., Saydah S., Imperatore G., DʼAgostino R.B. Jr, Mayer-Davis E.J., Pihoker C.; SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group. Trends in the prevalence of ketoacidosis at diabetes diagnosis: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Pediatrics. 2014 Apr. 133(4). e938-45. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-2795.
- Daly J. M., Reynolds J., Thorn A. et al. Immune and metabolic effects of arginine in the surgical patient. Ann. Surgery. 1988. 206. № 4. P. 512-523.
- Datrick P. S., Souba W. W. The role of glutamine in nutrition. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. 1991. 7. P. 229-305.
- Dhar I., Dhar A., Wu L., Desai K. Arginine attenuates methylglyoxal and high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress by an endothelial nitric oxide synthase-independent mechanism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therapeut. 2012. 342..196-204.
- Dhatariya K.K., Glaser N.S., Codner E., Umpierrez G.E. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 May 14. 6(1). 40. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0165-1.
- Dhatariya K.K. Defining and characterising diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Diabetes Res Clin. Pract. 2019 Sep. 155. 107797. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107797.
- Dubó S., Gallegos D., Cabrera L., Sobrevia L., Zúñiga L., González M. Cardiovascular action of insulin in health and disease: endothelial L-Arginine transport and cardiac voltage-dependent potassium channels. Front. Physiol. 2016. 7. 74.
- Evans K. Diabetic ketoacidosis: update on management. Clin. Med. (Lond.). 2019 Sep. 19(5). 396-398. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.2019-0284.
- Fasanmade O.A., Odeniyi I.A., Ogbera A.O. Diabetic ketoacidosis: diagnosis and management. Afr. J. Med. Med Sci. 2008 Jun. 37(2). 99-105.
- Fazeli Farsani S., Brodovicz K., Soleymanlou N., Marquard J., Wissinger E., Maiese B.A. Incidence and prevalence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D): a systematic literature review. BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 1. 7(7). e016587. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016587. Erratum in: BMJ Open. 2017 Sep 1;7(8):e016587corr1.
- Gasmi Benahmed A., Gasmi A., Arshad M., Shanaida M., Lysiuk R., Peana M., Pshyk-Titko I., Adamiv S., Shanaida Y., Bjørklund G. Health benefits of xylitol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020 Sep. 104(17). 7225-7237. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10708-7.
- Gibb F.W., Teoh W.L., Graham J. et al. Risk of death following admission to a UK hospital with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetologia. 2016. 59. 2082-2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-016-4034-0.
- Goldenberg J.Z., Day A., Brinkworth G.D., Sato J., Yamada S., Jönsson T., Beardsley J., Johnson J.A., Thabane L., Johnston B.C. Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished randomized trial data. BMJ. 2021 Jan 13. 372. m4743. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4743.
- Hoang H.H., Padgham S.V., Meininger C.J. L-arginine, tetrahydrobiopterin, nitric oxide and diabetes. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2013. 16(1). 76-82.
- Hu S., Han M., Rezaei A., Li D., Wu G., Ma X. L-arginine modulates glucose and lipid metabolism in obesity and diabetes. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017. 18(6). 599-608.
- Jefferies C.A., Nakhla M., Derraik J.G., Gunn A.J., Daneman D., Cutfield W.S. Preventing Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Pediatr. Clin. North. Am. 2015 Aug. 62(4). 857-71. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2015.04.002.
- Joint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group. The management of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. 2nd edition. 2013. http://www. diabetologists-abcd.org.uk/JBDS/JBDS_IP_DKA_Adults_Revised.pdf.
- Karslioglu French E., Donihi A.C., Korytkowski M.T. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome: review of acute decompensated diabetes in adult patients. BMJ. 2019 May 29. 365. l1114. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l1114.
- Lucotti P., Setola E., Monti L.D., Galluccio E., Costa S., Sandoli E.P., Fermo I., Rabaiotti G., Gatti R., Piatti P. Beneficial effects of a long-term oral L-arginine treatment added to a hypocaloric diet and exercise training program in obese, insulin-resistant type 2 diabetic patients. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006 Nov. 291(5). E906-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00002.2006.
- Maletkovic J., Drexler A. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2013 Dec. 42(4). 677-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.07.001.
- Monti L.D., Setola E., Lucotti P.C.G., Marrocco-Trischitta M.M., Comola M., Galluccio E. et al. Effect of a long-term oral L-arginine supplementation on glucose metabolism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012. 14. 893-900.
- Nyenwe E.A., Kitabchi A.E. The evolution of diabetic ketoacidosis: An update of its etiology, pathogenesis and management. Metabolism. 2016 Apr. 65(4). 507-21. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.007.
- Sivanandan S., Sinha A., Jain V., Lodha R. Management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2011 May. 78(5). 576-84. doi: 10.1007/s12098-010-0294-8.
- Umpierrez G.E., Kitabchi A.E. Diabetic ketoacidosis: risk factors and management strategies. Treat. Endocrinol. 2003. 2(2). 95-108. doi: 10.2165/00024677-200302020-00003.
- Wang Z.H., Kihl-Selstam E., Eriksson J.W. Ketoacidosis occurs in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes — a population-based study from Northern Sweden. Diabet Med. 2008 Jul. 25(7). 867-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02461.x.
- Галушко О.А., Недашківський С.М., Бабак С.І., Дяченко С.П. Сучасні можливості інфузійної терапії у хворих на діабетичний кетоацидоз. Здоров’я України. Тематичний номер «Діабетологія. Аспекти лікування». 2020. № 2. С. 2-4.
- Криворчук І.Г., Лещишин І.М. Корекція стресової гіперглікемії в хірургічних пацієнтів із метаболічним синдромом. Український журнал Перинатологія і Педіатрія. 2020. 3(83). 26-30. doi 10.15574/PP.2020.83.26.
- Курсов С.В., Никонов В.В. Стрессовая гипергликемия: обсуждение пути ее устранения с помощью применения многоатомных спиртов. Медицина невідкладних станів. 2019. № 4(99). С. 30-37.
- Курята О.В., Гречаник М.М. Роль L-аргініну в лікуванні серцево-судинних захворювань: у фокусі — вибір ефективної дози. Здоров’я України. 2019. № 11(456). С. 17-18.
- Лахно І.В. Можливості використання препаратів ксилітолу та L-аргініну у менеджменті менопаузи. Репродуктивне здоров’я жінки. 2021. № 2(47). С. 64-68. DOI: https://doi.org/10.30841/2708-8731.2.2021.232554.
- Прудіус П.Г., Скомаровський В.В., Катрук Л.Ю., Ніжинська-Астапенко З.П., Геранін С.В. Використання препарату Ксилат® у хворих з декомпенсованим цукровим діабетом. Острые и неотложные состояния в практике врача. 2010. № 3. С. 26-27.
- Соколова Л.К., Пушкарьов В.М., Тронько М.Д. L-аргінін у нормі та патології. Ендокринологія. 2019. 24. № 4. DOI: 10.31793/1680-1466.2019.24-4.373.
- Степанов Ю.М., Кононов И.Н., Журбина А.И., Филиппова А.Ю. Аргинин в медицинской практике (обзор литературы). Журн. АМН України. 2004. Т. 10. № 1. С. 340-352
- Шлапак І.П., Маньковський Б.М., Галушко О.А., Кондрацька І.М. Інфузійна терапія в практиці лікаря-ендокринолога. К., 2016. 294 с.
- Шлапак І.П., О.А.Галушко, Б.Ф.Яковлєв. Застосування нового комплексного препарату Ксилат® при ускладненому перебігу цукрового діабету. Ліки України. 2007, Травень. С. 66-68